スクレイピングとは何か?とイメージがつかない人に向けて書いています。
動作をみることから始めることで、イメージづくりを行います。
コピー&ペーストでスクレイピングの動きを確認します。
コードを貼り付けて実行して、動作を確認してみます。
スクレイピングする対象は本サイトのトップページ(https://pattern-life.com/)にします。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import bs4,requests
def Web_scraping():
###スクレイピングしたいサイトのURLを入れる
Target = "https://pattern-life.com/"#当サイトのURL
html = requests.get(Target)
soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(html.text, 'html.parser')
###取得したいデータを指定する
#サイト名を取得
Web_name = soup.find('h1',class_="sitename").text
print('【サイト名】')
print(Web_name.replace("\t",""))
#print(Web_name.replace("\t",""))#加工するときれいに取得できる(先頭の#を除去
#記事タイトルを取得
Contents_title = soup.find_all('h3')
Contents_title_child = []
num = 0
print("\n\n" + '【記事のタイトル】')
for count in Contents_title:
Contents_title_child.append(count.text)
#Contents_title_child.append(count.text.replace("\t",""))#加工するときれいに取得できる(先頭の#を除去
print(Contents_title_child[num])
num = num + 1
### <プログラム開始> ###
if __name__ == '__main__':
Web_scraping()
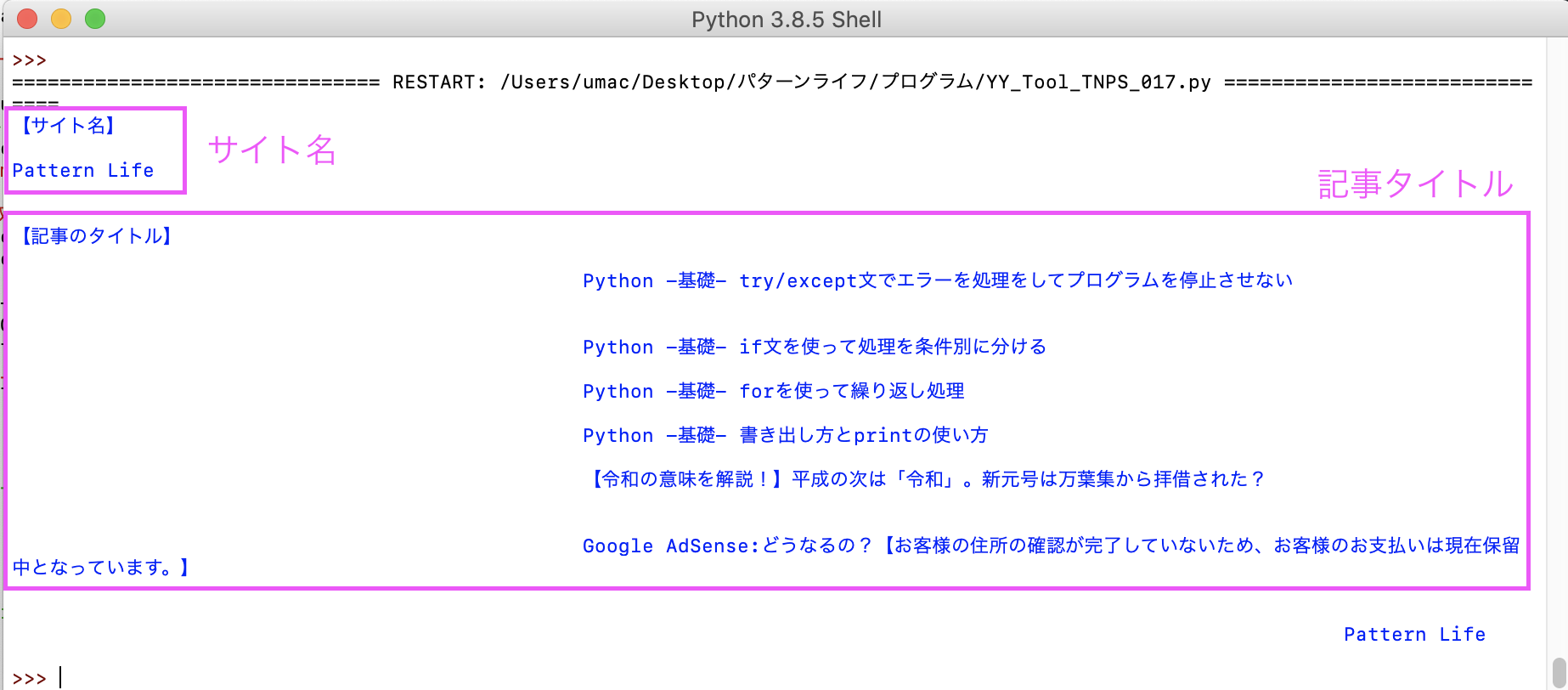
結果はこのようになっていればOKです。(記事タイトルは更新されている場合があります)
ここから解説。
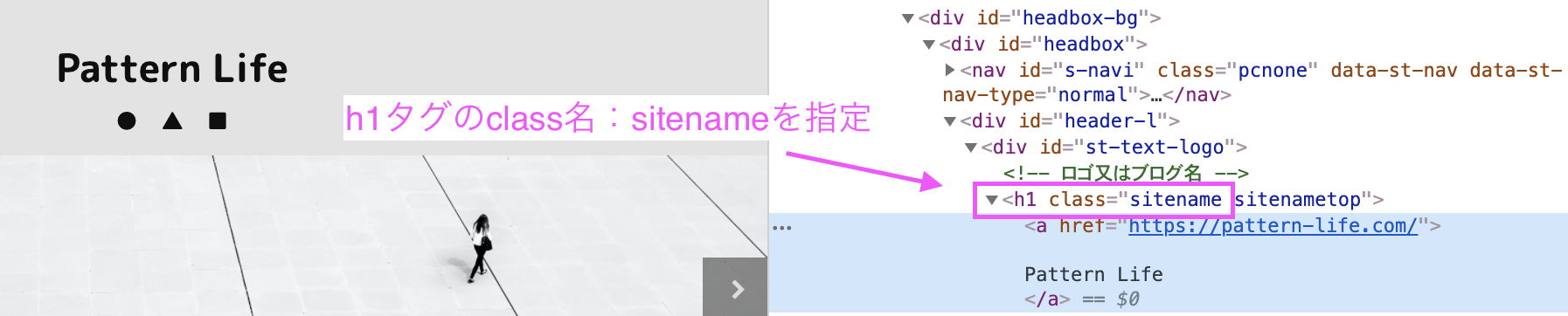
サイト名はh1タグのclass名:sitenameを指定して、textを取得しています。
<コード>Web_name = soup.find(‘h1’,class_=”sitename”).text
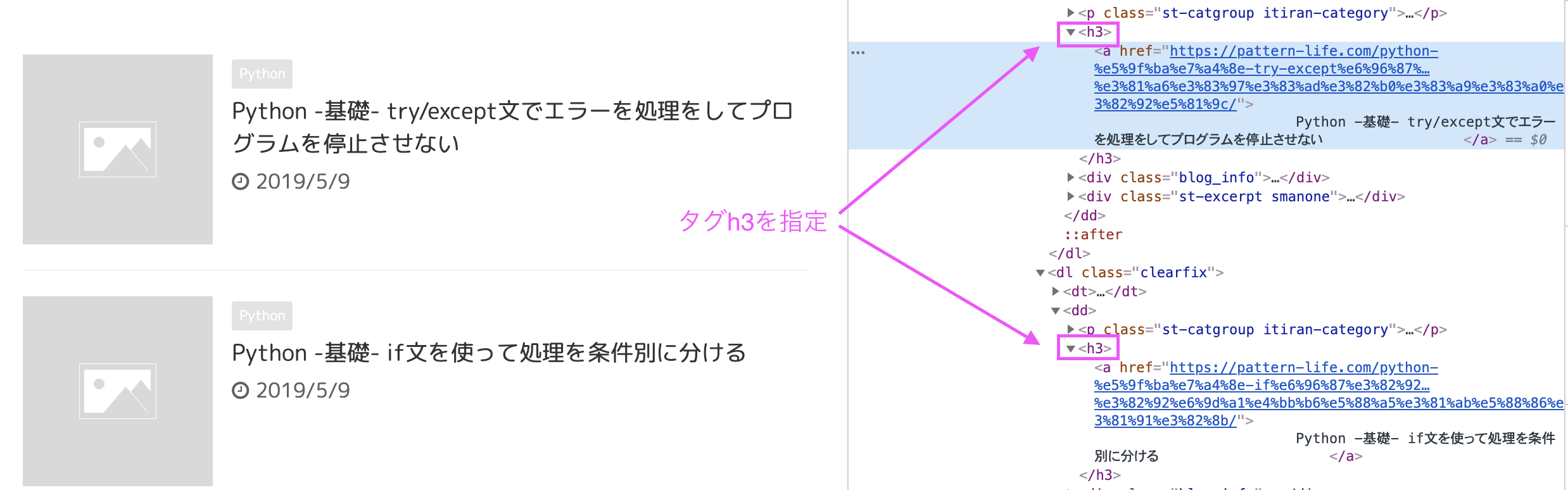
記事タイトルはh3タグを指定して、
<コード>Contents_title = soup.find_all(‘h3’)
textを順番にリストに入れています。
<コード>Contents_title_child.append(count.text)